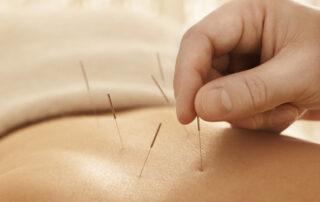
Acupuncture may curb the heightened risk of stroke associated with rheumatoid arthritis
Effects independent of sex, age, medication use, and co-existing conditions Needling may reduce pro-inflammatory proteins in the body, suggest researchers A course of acupuncture may curb the heightened risk of stroke associated with rheumatoid arthritis, finds a comparative study published in the open access journal BMJ Open. The effects seem to ...